- Contact angles of different substrates:
- Measure the contact angle of water on 5 samples: aluminum, copper, PVC, Teflon, glass. Use Table 1.
- Determine the effect of surface modification of copper on the contact angle of water:
- Immerse a Cu disk in 30% H2O2 solution for 30 minutes in a covered plastic cup.
- Rinse with de-ionized water and dry carefully.
- Measure the contact angle of water on the surface.
- Immerse a Cu disk in 20mM sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), which is a monosulfate salt, in ethanol for 30 minutes in a covered plastic cup.
- Rinse with ethanol and dry carefully.
- Measure the contact angle of water on the surface.
- Create a Zisman plot for n-propanol/water solutions on Teflon:
- Make sure you are familiar with the Zisman plot paper.
- Prepare n-propanol/water solutions of concentrations calculated during the lab preparations.
- Measure the contact angle on a Teflon substrate.
In order to use a single disk for all measurements, the mixtures must be measured in ascending order of concentration. - Calculate γLG using the following equation:
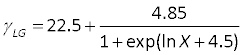
Remember that this equation is true only for 0.001 ≤ X ≤ 1, where X is the molar fraction of alcohol in water. Plot γLG as a function of cos(θ) and extract γSG.
- Determine the effect of surfactant (Triton X-100) on water surface tension:
- Make sure you are familiar with the CMC paper.
- Measure the contact angle of Triton X-100/water solutions of different concentrations on a Teflon substrate. The initial concentration of the Triton X-100 solution is 5mM. Record the contact angles for each solution in Table 2.
- Calculate γLG (γWA) using the following equation:
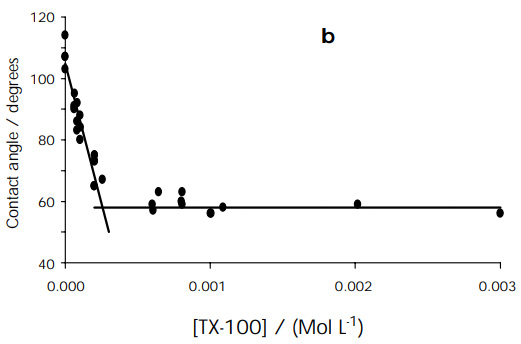
- Calculate γSL using Young's equation: γSG = γSL + γLG cos(θ) and the value of γSG you calculated in procedure 3. A typical plot of Teflon contact angle dependence on surfactant concentration is shown in Figure 1.
Table 2: Contact angle dependence on surfactant concentration
C[M]
Contact angle [degree]
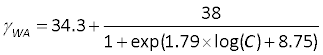
Table 1: Contact angles of water on different surfaces
|
Sample |
Contact angle [degrees] |
|
Aluminum |
|
|
Cu |
|
|
PVC |
|
|
Teflon |
|
|
Glass |
|