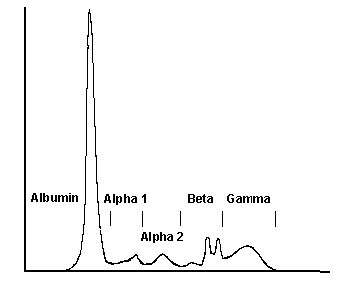
| Globulins -- The blood proteins can be roughly divided into two categories: albumin, which is the predominant protein that provides most of the oncotic pressure within the bloodstream, and globulins. The globular proteins were traditionally separated by serum electrophoresis, which produced three subcategories |
 |
| |
Alpha globulins - This fraction contains proteins that act as carriers of substances in the blood. Some are in high enough concentration to measure in a serum specimen. A protein in the alpha 1 fraction is alpha-1-antitrypsin, a protease inhibitor. Proteins in the alpha 2 fraction include ceruloplasmin, which carries copper, and haptoglobin, which binds free hemoglobin. Alpha-2-macroglobulin is another protease inhibitor also found here. |
| |
Beta globulins - This fraction contains proteins that act as carriers of substances in the blood. Some are in high enough concentration to be measured in a serum specimen. Two such proteins are transferrin, which carries iron, and beta-2 microglobulin, which links with the class 1 MHC molecule. The complement component C3 may produce a small peak as well. |
| |
Gamma globulins - This fraction contains the globular proteins that act as antibodies. These can be further quantified as IgG, IgA, and IgM (IgD and IgE are in very small quanitities). Normally, antibodies are made to a variety of antigens (polyclonal response), so the peak is broad. A tall, narrow peak suggests a monoclonal "spike" of abnormal immunoglobulin. |
| Complement - Complement is not one substance, but a set of proteins that circulate in the blood. Some of the components are pre-formed, while others are generated during immune responses. Complement is continually being manufactured and degraded. Some of the components, such as C3 and C4, can be measured in a regular serum specimen. |
| C-reactive protein - This is a protein that binds to polysaccharides present on the surfaces of many bacteria, fungi, and protozoal parasites. It also binds to phosphocholine, phosphatidylcholines such as lecithins, and polyanions such as nucleic acids. Once complexed, CRP becomes an activator of the classical complement pathway. CRP recognizes potentially toxic autogenous substances released from damaged tissues, binds them, and then detoxifies or clears them from the blood. |
| Coagulation factors - The coagulation system often works in concert with immune responses that are part of inflammatory reactions. It is complex and will be discussed elsewhere. |
|